Cancer is an anxiety and fear-inducing diagnosis, yet thousands of American adults, seniors, and children are diagnosed with some form of cancer or tumor annually. According to the National Cancer Institute, over 1.8 million new cases of cancer were diagnosed in the United States in the year 2020. There are a variety of treatment options including surgery, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. One cancer treatment option is continuing to advance past the others with fast treatment, faster recovery and continuously improving success rates: radiation therapy.
Radiation Therapy of the Past
Traditional radiation therapy for cancer treatment was often a supplemental treatment to prevent recurrent cases. It was also a secondary cancer treatment option for patients that didn’t qualify for surgery or had very weak immune systems, such as seniors. The radiation was either applied from an outside source, known as external beam radiation or administered in a solid or liquid to be put inside the body, known as internal radiation therapy.
The concerns with radiation in these forms were control and safety. Traditional external beam radiation could be targeted to a general region, however many of the healthy cells and tissues would also be destroyed by the radiation. Internal radiation therapy applied a low dose of radiation, but it affected the entire body.
As technology advanced, radiation therapy began to improve the control and targeting of cancer cells. Today, there are radiation therapy options that can be dialed down to the centimeter for extreme accuracy and minimal damage to healthy tissue.
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Cancer Treatment

From brain tumors to prostate/ ovarian cancers, radiation therapy has become a highly suitable treatment option for patients. While the current capabilities make radiation suitable for cancers below stage 3, radiation oncologists are optimistic about current radiation therapy machines as well as the future development of radiation technology.
One radiation treatment approach is changing the way radiation is mapped and applied to the patient. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) uses high doses of radiation applied by a highly concentrated beam. This type of radiation requires fewer treatments because the radiation is more powerful and focused. According to the UCLAHealth website, one session of SBRT radiation therapy is “more biologically effective than 6 weeks of incremental doses of radiation daily.” This eliminates the longer period of radiation that has characterized more traditional approaches.
The treatment process is also much easier on the patient, lasting only about 45 minutes to an hour, with little to no downtime following the procedures. Unlike chemotherapy and surgery that can take weeks to recover from, SBRT has minimal side effects and requires no recovery time. Many patients are able to return home or to work without skipping a beat. These attributes along with the high success rates have made SBRT a very popular form of radiation therapy among patients and physicians.
SBRT also became superior to traditional radiation. Traditional radiation therapies map a large field where the tumor is, but a portion of the tumor could still lie outside of the targeted region. They also utilize 2D imaging to identify the location of the tumor. Because of this, very low doses of radiation could be administered per session. To obtain the ideal results, traditional radiation could require between 30 – 45 treatment sessions per tumor. Even after the final treatment, a portion of the tumor could still exist, and the healthy surrounding tissues would likely be adversely affected. After months of treatment, a patient hearing this news would be disheartened and worried for the future of their health.
Tumors in the breasts or lungs could be even more difficult to track since the movement from the patient’s breathing would likely cause the tumor to move. SBRT proved to be especially beneficial for these patients and improved their rates of success and decreased their chances of recurring cancer.
SBRTs Like CyberKnife Radiation Therapy Provide Military-Grade Accuracy.
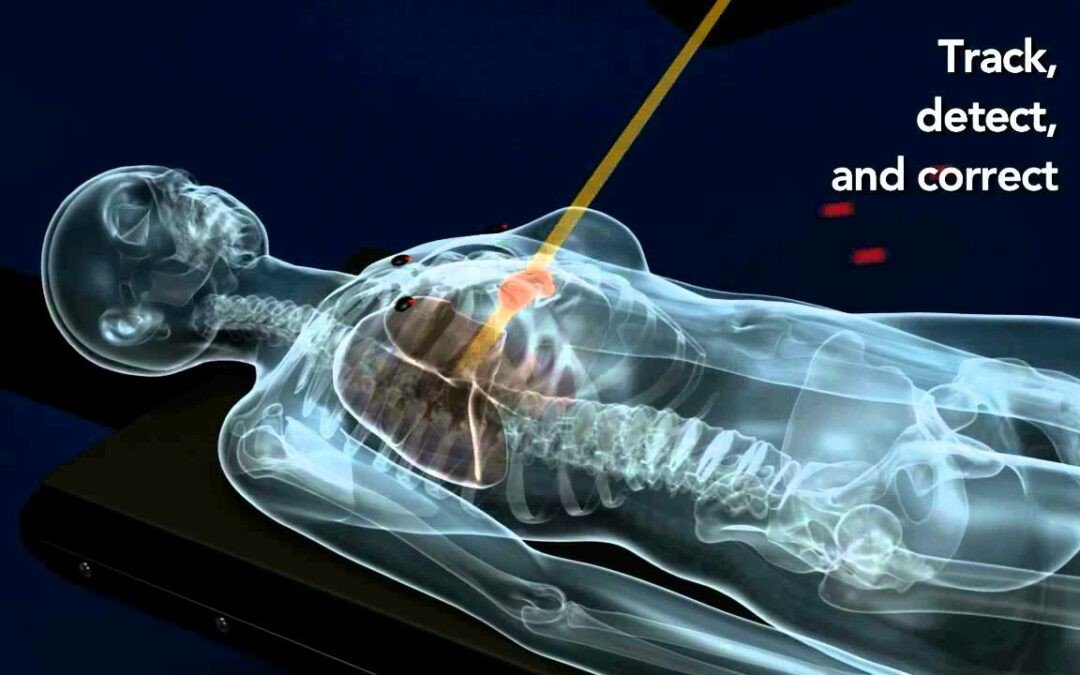
With the development of SBRT technologies, a variety of radiation administration machines began to build upon this high-dose, highly targeted radiation therapy. Several companies such as the CyberKnife System by Accuray began using 4D imaging and tracking technology and robotic “arms” that had the ability to move and “follow” the tumor.
Radiation oncologist and the Medical Director of the CyberKnife Center in Miami, Dr. Mark Pomper explained,
“CyberKnife is the most advanced radiosurgery technique available for the treatment of cancerous and non-cancerous lesions and tumors throughout the body.
Over the last decade, the CyberKnife Center of Miami has treated more than 3,500 patients with highly successful outcomes. This revolutionary treatment has helped save many lives while maintaining patients’ quality of life. That’s why we like to call it The Beam of Life.”
CyberKnife is a minimally invasive cancer treatment option that can provide successful elimination for a variety of cancers including brain tumors, breast cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic, kidney, liver, ovarian, spinal tumors, and much more. It’s incredibly precise and provides patients with a fast, effective solution to get them back to enjoying their life without diminishing the quality of life

